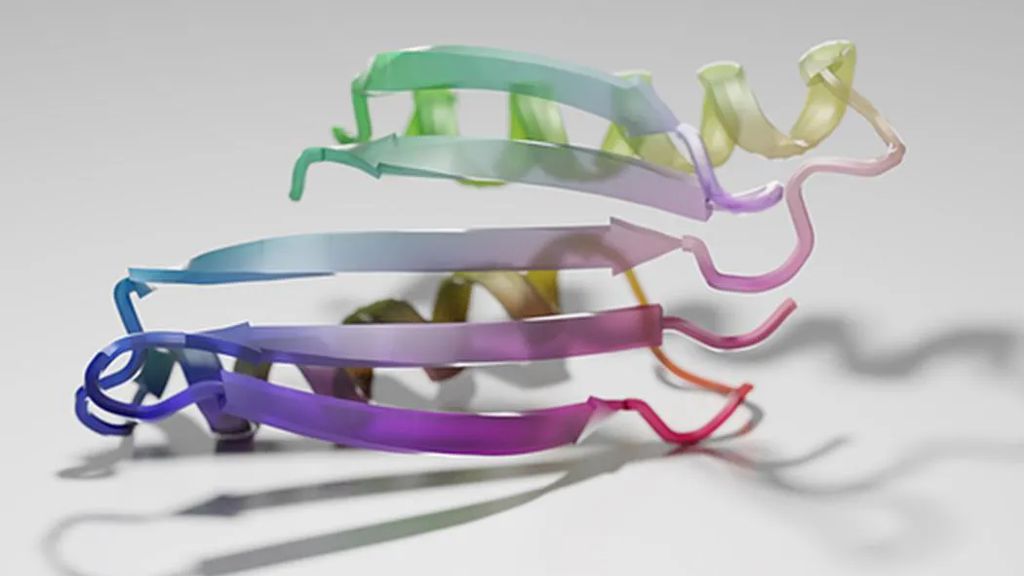
By getting artificial intelligences to hallucinate, scientists are creating novel proteins with an unlimited array of properties, a new study finds.
Proteins, which are strings of molecules found in every cell, spontaneously fold into complex 3-D shapes that are key to nearly every biological process. However, the intricacy of the interactions between the amino acids comprising each protein makes it difficult to predict their structures, even if researchers know the sequence of amino acids that constitute a protein.
Scientists have long employed programs such as Rosetta to design new proteins with potentially novel functions, to model how they might fold, and to predict if they might behave as hoped. Increasingly, deep neural networks are also helping researchers predict protein structures.
Now, scientists have found that a deep network trained exclusively to model protein shapes can also dream up proteins with new structures. They detailed their findings in the 2 December issue of the journal Nature.
The researchers, collaborators from several U.S.-based academic institutions, experimented with trRosetta, a web-based platform for protein structure prediction powered by deep learning and Rosetta. They gave it completely random protein sequences and introduced mutations into them until trRosetta began making generalizations that yielded predictions about how the strings of amino acids would arrange themselves into stable 3D structures.
“It took just a couple days to implement a pilot version of the protocol and qualitatively check whether the produced outcomes look viable,” says study lead author Ivan Anishchenko, a computational biologist at the University of Washington at Seattle. “We were delighted to see that the hallucinated proteins looked plausible by eye and were also quite diverse structurally. It is highly desirable of an automated protein generation procedure to have both these properties.”
The scientists generated 2,000 new protein sequences, each 100 amino acids long. All of them were originally figments of the AI’s imagination.