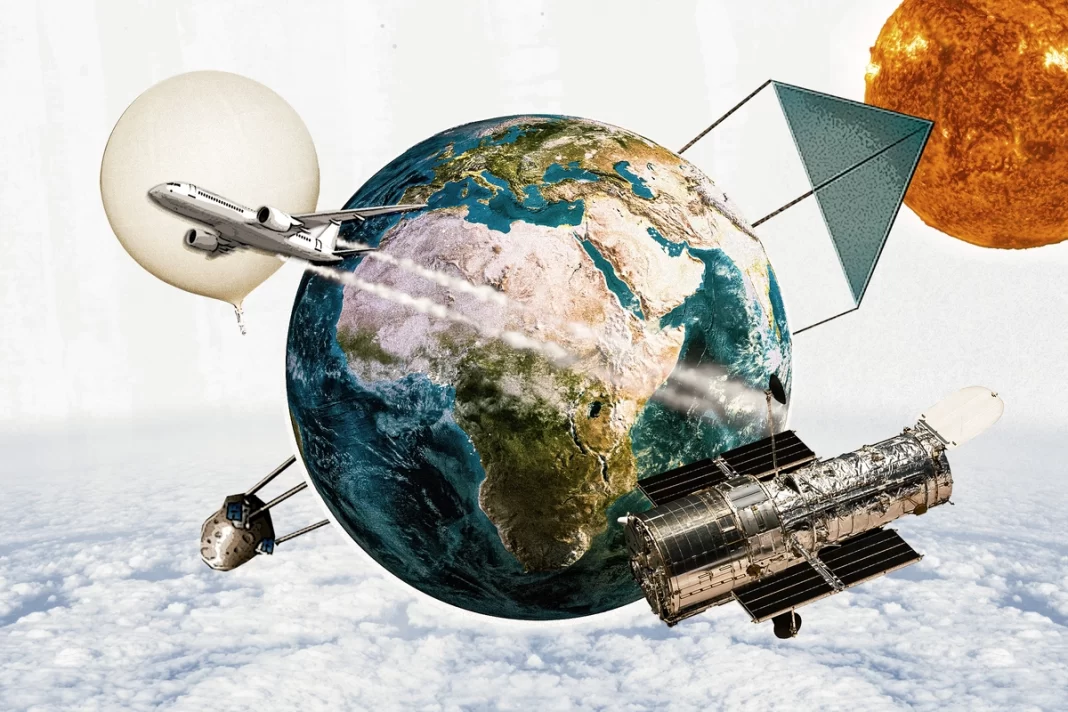
An American company is already sending balloons filled with sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere. NASA is considering flying ice into the atmosphere.
The Earth is too hot and only getting hotter, according to governments and global bodies such as the United Nations; and the efforts to reduce carbon dioxide aren’t having enough of an effect.
“The world is passing through the 1.5°C ceiling and is headed much higher unless steps are taken to affect Earth’s energy imbalance,” James Hansen, the previous director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, warned in January.
Thus, to buy more time, on Feb. 28, scientists from NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) released a report detailing a solution called “intentional stratospheric dehydration,” or in layman’s terms, flying planeloads of ice to 58,000 feet and spraying ice particles into the upper atmosphere.
“It’s a very small effect,” said lead author Joshua Schwarz, a research physicist at NOAA’s chemical sciences laboratory. “Pure water vapor doesn’t readily form ice crystals. It helps to have a seed, a dust particle, for example, for ice to form around.”
The researchers report that by dispersing small particles, or what it calls ice nuclei, into areas of the atmosphere that are both “very cold and super-saturated with water vapor,” water vapor in the atmosphere will “freeze-dry” and rain out of the atmosphere as ice crystals, cooling the planet.
The proposal is known as geoengineering—and NASA and NOAA’s joint plan is far from the only idea that’s jumped from the pages of science fiction, à la the 2013 Hollywood film “Snowpiercer,” to mainstream science.
István Szapudi, an astronomer at the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy, has turned to essentially geoengineering a giant parasol, or what he calls, a “tethered solar shield” to shield the Earth from a portion of the sun’s energy.
“Any sunshield works by blocking a small fraction, circa 1–2 percent, of sunlight reaching Earth,” Mr. Szapudi told The Epoch Times. “This is an almost undetectable amount by looking at the sun, but it would still cool the atmosphere to pre-industrial temperatures according to climate models.
By Katie Spence