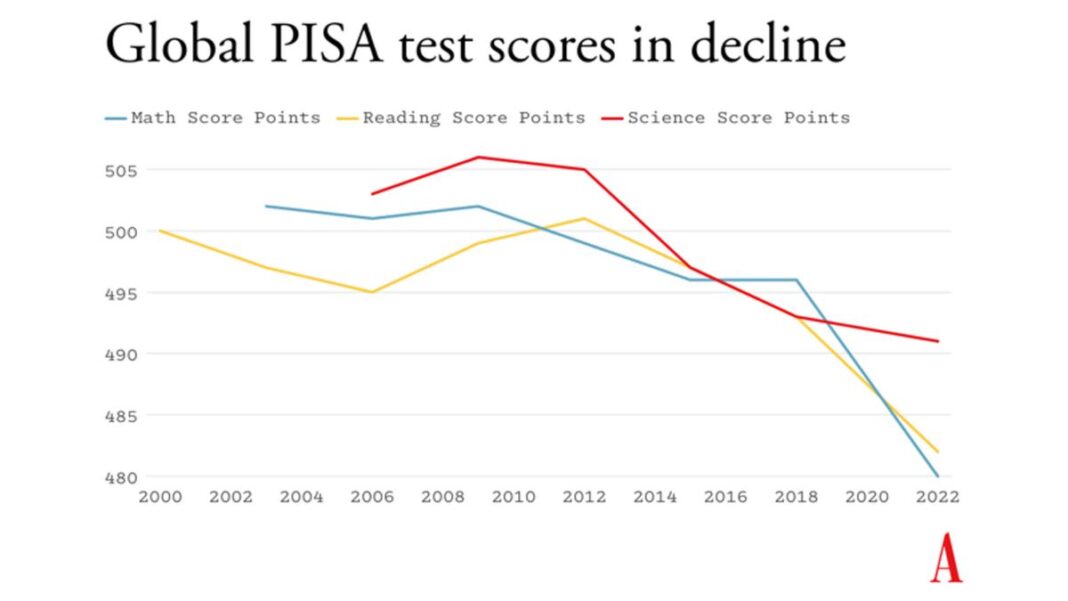
Test scores have been falling for years—even before the pandemic.
This is Work in Progress, a newsletter about work, technology, and how to solve some of America’s biggest problems. Sign up here.
For the past few years, parents, researchers, and the news media have paid closer attention to the relationship between teenagers’ phone use and their mental health. Researchers such as Jonathan Haidt and Jean Twenge have shown that various measures of student well-being began a sharp decline around 2012 throughout the West, just as smartphones and social media emerged as the attentional centerpiece of teenage life. Some have even suggested that smartphone use is so corrosive, it’s systematically reducing student achievement. I hadn’t quite believed that last argument—until now.
The Program for International Student Assessment, conducted by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development in almost 80 countries every three years, tests 15-year-olds in math, reading, and science. It is the world’s most famous measure of student ability. Most years, when the test makes contact with American news media, it provides instant ammunition for critics of America’s school system, who point to PISA scores and ask something like “Why are we getting crushed by Finland in reading?” or “Why are we getting smoked by Korea in math?”
The latest PISA report has a different message. Yes, Americans scored lower in math than in any other year in the history of the test, which began in 2003. (Once again, the test recorded America’s persistent inequalities; Black and Hispanic students, on average, scored below Asian and white students, who typically do about as well as their peers around the world.) But COVID learning loss was even worse elsewhere, creating what the authors of the PISA report called “an unprecedented drop in performance” globally that was “nearly three-times as large as any prior change.”
[Jonathan Haidt: Get phones out of schools now]
The deeper, most interesting story is that test scores have been falling for years—even before the pandemic. Across the OECD, science scores peaked in 2009, and reading scores peaked in 2012. Since then, developed countries have as a whole performed “increasingly poorly” on average. “No single country showed an increasingly positive trend in any subject,” PISA reported, and “many countries showed increasingly poor performance in at least one subject.” Even in famously high-performing countries, such as Finland, Sweden, and South Korea, PISA grades in one or several subjects have been declining for a while.
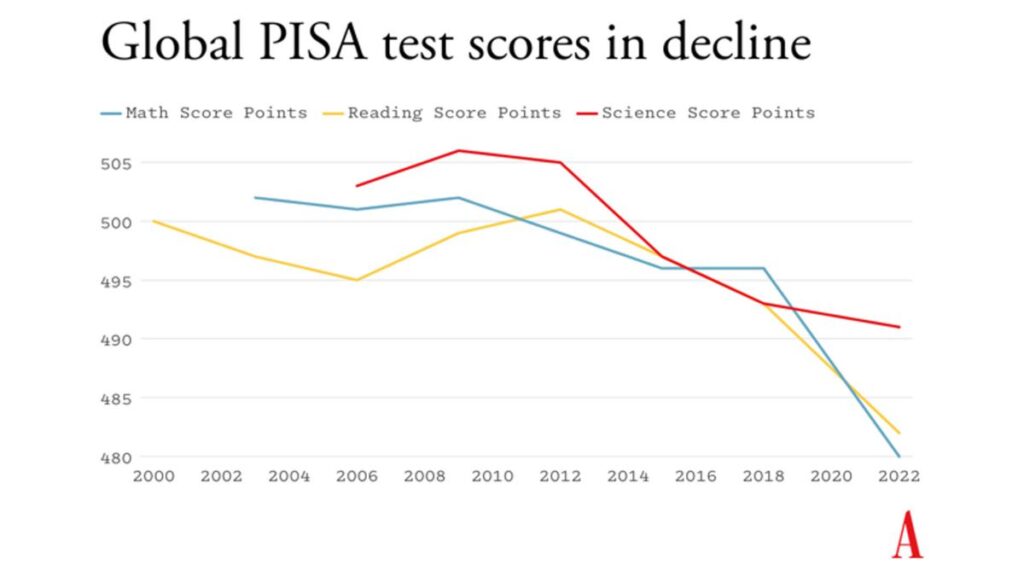
So what’s driving down student scores around the world? The PISA report offers three reasons to suspect that phones are a major culprit.
First, PISA finds that students who spend less than one hour of “leisure” time on digital devices a day at school scored about 50 points higher in math than students whose eyes are glued to their screens more than five hours a day. This gap held even after adjusting for socioeconomic factors. For comparison, a 50-point decline in math scores is about four times larger than America’s pandemic-era learning loss in that subject.
Second, screens seem to create a general distraction throughout school, even for students who aren’t always looking at them. Andreas Schleicher, the director of the PISA survey, wrote that students who reported feeling distracted by their classmates’ digital habits scored lower in math. Finally, nearly half of students across the OECD said that they felt “nervous” or “anxious” when they didn’t have their digital devices near them. (On average, these students also said they were less satisfied with life.) This phone anxiety was negatively correlated with math scores.
In sum, students who spend more time staring at their phone do worse in school, distract other students around them, and feel worse about their life.