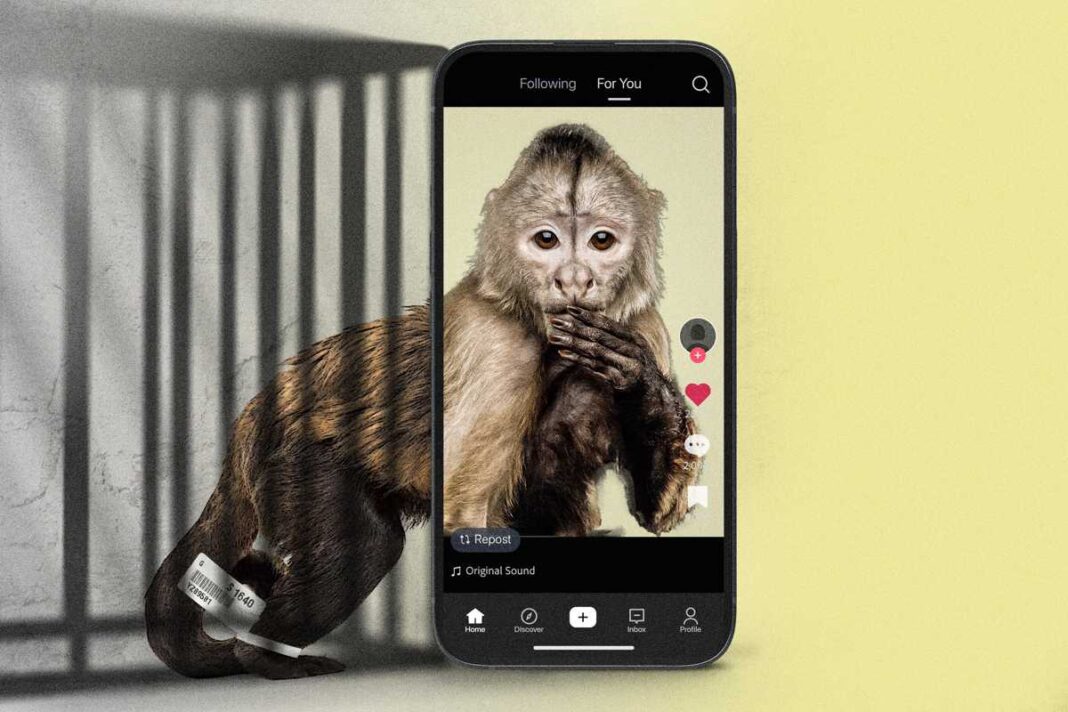
Critics say social media often presents a false image of the pet’s actual needs and the reality of their temperament, leading to a slew of abandonments.
The global trade in pet monkeys and primates is being mainly driven by greed and social media, says wildlife protection advocate Nina Plail.
It’s a familiar pattern: people see a warm and fuzzy baby primate online and decide they want one for a pet.
Wild baby monkeys are “adorable,” Ms. Plail said, but their cuteness fades as they grow older and become aggressive.
Many primates will attack their owners once they reach sexual maturity at around two years old, or the owner may not realize the amount of work required to care for an adult primate.
“When bonded with a human, they’re going to cling to them like their mother. They’re going to be amazing,” Ms. Plail told The Epoch Times.
“But when they reach maturity, they almost always get aggressive. They start biting. They start singling out people in the family they don’t like. They sometimes start seeing their human caregiver as a mate, and they attack anyone who comes near.”
Once this happens, unruly primates usually end up in wildlife sanctuaries as unwanted pets or disappear.
“No human can meet the social needs of a monkey. These animals [exist] to be on the tops of trees,” she said.
Ms. Plail said she has received more than a dozen pet monkeys surrendered in the past two years to Chase Animal Rescue and Sanctuary in Webster, Florida.
In each case, the owner no longer wanted the primate because it became aggressive or was too difficult to manage.
“For one small sanctuary in the middle of nowhere, it’s a large number,” said Ms. Plail, who is the director of the sanctuary.
“For sanctuaries like ours, it probably costs us $10,000 to build a new enclosure” to house each primate.
Social media plays a significant role in the global online market for pet primates, both legally and in the black market, she said. According to some estimates, the international trade in wild primates, which remains largely unregulated, generates between $117 million and $138 million annually.
By Allan Stein