Over half of all women and about 12 percent of men will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing pain and burning with urination. If left untreated, UTIs may lead to worsening symptoms and further complications.
UTIs are very common in women and not uncommon in men. Approximately 50 percent to 60 percent of all women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime, while about 12 percent of men will. Globally, the incidence of UTIs has increased from about 252 million reported cases in 1990 to about 404 million in 2019.
According to the Urology Care Foundation, UTIs are the second most common type of infection in the body and are the reason for over 8 million doctor visits each year.
While most UTIs are not serious and can be easily treated, they can be dangerous if the infection travels to the kidneys and enters the bloodstream, leading to sepsis.
“A UTI is often thought of as being a minor issue, but it can be life-threatening. It’s not anything to take lightly. Even if the symptoms are minor, you need to get it taken care of,” Dr. Jennifer J. Bryan said on an American Medical Association site.
What Are the Types of UTIs?
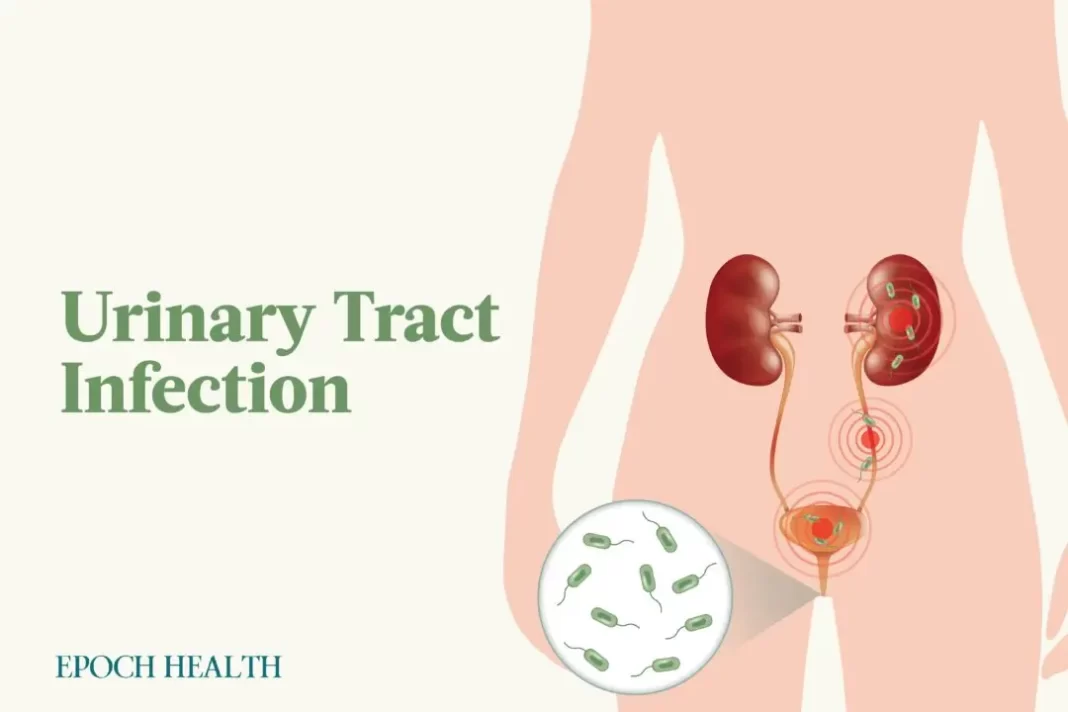
The urinary tract comprises the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. A UTI may affect the urethra (causing urethritis), the bladder (causing cystitis), or the kidneys (leading to pyelonephritis).
Most UTIs are considered “lower UTIs” because they affect the lower urinary tract (the bladder and urethra). A UTI that has progressed through the ureters (which are the tubes leading to the kidneys) into the kidneys is called an “upper UTI” and requires aggressive treatment.
What Are the Symptoms and Early Signs of a UTI?
Symptoms and signs of a UTI may include the following:
- A burning sensation when urinating.
- An urgent need to urinate.
- Bloody or cloudy urine.
- Frequent urination.
- Pressure or pain in the lower abdomen.
- Bad-smelling urine.
The location of the infection may result in varying symptoms, such as the following:
- Kidneys: back or side pain, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting.
- Bladder: pelvic pressure, lower abdomen discomfort, frequent and/or painful urination, blood in urine.
- Urethra: burning sensation during urination, discharge.
UTIs in young children and older people may be more challenging to diagnose because these populations may not exhibit typical symptoms or may have trouble communicating their symptoms.